The Thriving in Midlife Report is a comprehensive piece, conducted in collaboration with Udemy, and it explores the fulfillment priorities of individuals aged 40 and above across five key pillars: Health, Fitness, Career, Relationships, and Legacy. It provides valuable insights into how midlife individuals perceive and pursue fulfillment in these areas, offering data-driven recommendations for optimizing their goals and well-being. Additionally, the report implies that fulfillment-centric-leadership results in more engaged employees and higher retention. This post summarizes key findings about workplace priorities for employees.
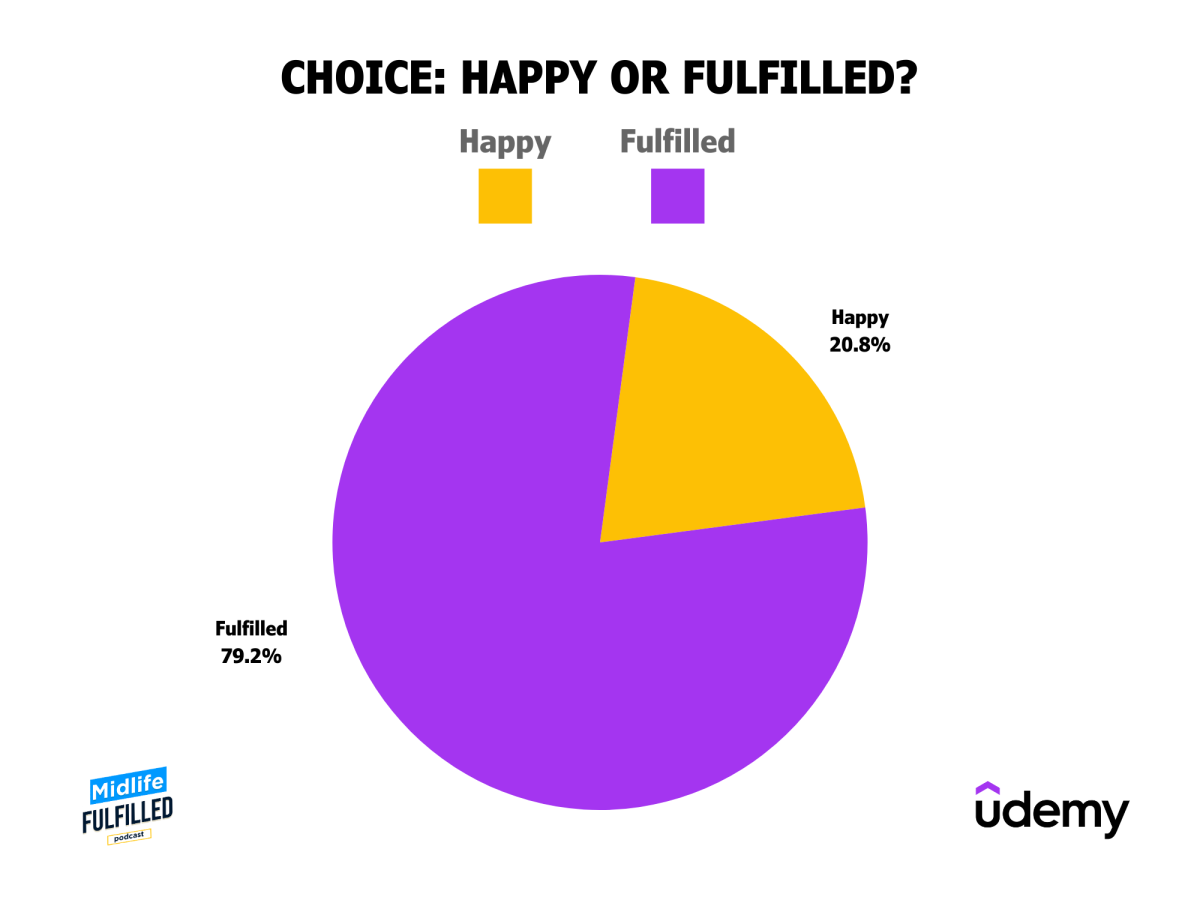
Fulfillment vs. Happiness
Midlife individuals prioritize fulfillment (a deeper sense of satisfaction and purpose) over fleeting happiness. 79.2% of respondents chose fulfillment if they could only choose one over the other, indicating a desire for meaning derived from activities, achievements, and contributions.
The Five Pillars of Midlife Fulfillment
Health: High fulfillment (65.7%), indicating effective health management for most.
Fitness: Lower fulfillment (47.3%) than health, revealing a challenge in maintaining fitness routines despite overall good health.
Career: Moderately high fulfillment (61.2%), but many still seek growth and leadership opportunities.
Relationships: Strong fulfillment (70%), with emphasis on nurturing connections and positive social interactions.
Legacy: Moderate fulfillment (53%), highlighting a desire for greater impact and a need for increased focus on legacy-building activities.
Age-Related Trends
30s-50s: High focus on career development and legacy building, with fitness often taking a backseat due to career and family responsibilities.
60s and Beyond: Career fulfillment shifts with retirement transitions, while legacy assessment and consolidation become paramount.
Personal Growth and Improvement
A majority of respondents actively prioritize personal growth (57.2%) and professional growth (54.3%), demonstrating a commitment to continuous self-improvement. A similar commitment is observed in intentions to improve physical health (50.2%) and less so in mental health (40.8%), with moderate engagement reported for fitness and relationship improvements.
Career Dynamics
Nearly half of respondents are employed by for-profit businesses (42.1%), followed by business owners with staff (17.7%) and sole proprietors (17.4%). There is a high emphasis on developing technical skills (49%) and communication skills (40%) to advance careers. Most feel valued for their skills (42.6%), indicating a workplace that recognizes expertise and talent.
Intergenerational Workplace Engagement
Positive engagement with younger generations is prevalent (75.7%), with most collaborating regularly. Collaboration is deemed extremely important for achieving workplace goals (58.3%), recognizing the value of diverse perspectives and knowledge transfer. Fewer respondents (37.4%) report actively seeking out opportunities to work with younger workers suggesting a leadership gap in intergenerational workplace engagement.
75.7% reported positive experiences when engaging with younger generations in the workplace. These positive experiences likely stem from benefits such as:
– Fresh perspectives
– Innovative ideas
– Learning opportunities
– Mentoring dynamics
The majority of respondents (58.7%) consider the talent of younger generations essential to their workplace’s success. They see their contributions as critical for:
– Innovation
– Problem-solving
– Achieving strategic objectives
Over half of the respondents (56.2%) believe that collaborating with younger generations is extremely important for achieving workplace goals. Almost another third (29.4%) find it somewhat important. 63% engage with younger generations as part of their daily work routine, while 25.3% engage occasionally based on project needs. Only a small percentage (2.8%) reported rarely engaging with younger generations at work.
Organizational Support for Intergenerational Collaboration
The report also highlights the importance of organizational support for fostering positive intergenerational relationships in the workplace.
33.4% of respondents said their workplace supports mentor/mentee relationships but does not formally arrange them. This suggests that mentorship often happens organically rather than through structured programs. 14.3% reported that their workplaces actively arrange mentorship relationships, indicating a commitment to fostering intergenerational learning and development. 20.2% of respondents said their workplaces do not engage in any form of mentorship. This presents an area for potential improvement, as mentorship can enhance workplace dynamics and employee satisfaction.
The Thriving in Midlife report also suggests a range of actionable steps for organizations to consider to improve intergenerational collaboration:
Implement cross-generational programs that facilitate knowledge exchange between generations. This could include mentorship and reverse-mentorship programs.
- Create opportunities for joint projects and team activities that require contributions from both younger and midlife employees, enhancing mutual respect and understanding.
- Provide training and development that caters to diverse age groups, focusing on skills relevant to both younger and midlife employees.
- Encourage open and respectful communication channels that allow employees of all ages to share ideas and feedback freely.
- Recognize and reward contributions from all generations, highlighting the value of diverse perspectives and skills in achieving organizational goals.
- Implement conflict resolution strategies that address generational misunderstandings and promote a cohesive work environment.
- By taking these steps, organizations can leverage the unique strengths of each generation, driving innovation, enhancing workplace satisfaction, and achieving long-term success.
The Fulfillment Centric Leadership™ model recognizes that when leaders prioritize fulfillment, they cultivate a work environment where employees experience meaningful growth, connection, and purpose. Unlike traditional management approaches, this model advocates for a holistic view of employees, emphasizing their well-being across key life pillars—Health, Fitness, Career, Relationships, and Legacy. Leaders who embody this philosophy empower their teams to set and achieve balanced goals within these areas, fostering a culture of authenticity, resilience, and loyalty. The Thriving in Midlife Report demonstrates that employees who feel supported in their pursuit of personal fulfillment are not only more engaged but also more likely to remain with an organization, thus reducing turnover and elevating the company’s appeal to high-caliber talent. By adopting Fulfillment Centric Leadership organizations can lead with empathy and foresight, driving both individual satisfaction and organizational success.